What Is the Best Diet for Recovering from Giardiasis?
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia. Common symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and fatigue.
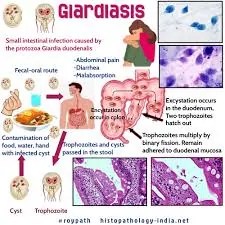
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia. Common symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and fatigue. Proper nutrition plays a vital role in recovery, as the right diet can help alleviate symptoms, restore digestive health, and prevent recurrence. This guide explores the best dietary strategies for giardiasis recovery, incorporating the importance of Nizonide 500mg as a treatment option.
Understanding Giardiasis and Its Impact on Digestion
Giardiasis disrupts the digestive system, leading to malabsorption of nutrients, dehydration, and weight loss. The infection inflames the intestinal lining, making it more challenging to digest and absorb certain foods. Addressing these issues through diet is essential to facilitate recovery and regain normal gut function.
Role of Nizonide 500mg in Giardiasis Treatment
Before diving into dietary recommendations, it’s important to mention the role of nizonide 500mg (nitazoxanide), a broad-spectrum antiparasitic medication often prescribed to treat giardiasis. This medication works by interfering with the energy metabolism of Giardia lamblia, effectively clearing the infection. While nizonide 500mg helps eliminate the parasite, a supportive diet enhances the healing process and promotes gut health.
Key Dietary Principles for Giardiasis Recovery
Hydration Is Crucial
Why? Diarrhea caused by giardiasis can lead to severe dehydration and loss of electrolytes.
What to Do
Drink plenty of fluids such as water, herbal teas, and oral rehydration solutions. Coconut water is an excellent natural option to replenish electrolytes.
Focus on Easily Digestible Foods
Why? Inflammation of the intestinal lining can make it difficult to digest complex foods.
What to Eat: Opt for bland, low-fiber foods such as white rice, boiled potatoes, and plain toast. These are gentle on the stomach and help reduce diarrhea.
Incorporate Probiotics
Why? Giardiasis often disrupts the balance of gut bacteria.
What to Eat: Include yogurt with live cultures, kefir, and fermented foods like sauerkraut or kimchi. Probiotics can help restore a healthy gut microbiome.
Avoid Trigger Foods
Why? Certain foods can exacerbate symptoms such as diarrhea and bloating.
What to Avoid: Stay away from dairy (if lactose intolerant), fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods.
Introduce Soluble Fiber Gradually
Why? Soluble fiber can help absorb excess water in the intestines and form firmer stools.
What to Eat: Oats, bananas, and applesauce are good sources of soluble fiber. These foods are also gentle on the stomach.
Sample Meal Plan for Giardiasis Recovery
Day 1
Breakfast: Plain oatmeal cooked with water, topped with a mashed banana.
Snack: Coconut water and a slice of plain toast.
Lunch: Boiled white rice with steamed carrots and a small portion of skinless chicken breast.
Snack: A cup of unsweetened applesauce.
Dinner: Baked fish with mashed potatoes and a side of steamed zucchini.
Day 2
Breakfast: Rice cereal with almond milk (if tolerated) and a small serving of blueberries.
Snack: A handful of plain crackers and a cup of peppermint tea.
Lunch: Lentil soup (blended for easier digestion) with a slice of gluten-free bread.
Snack: Probiotic yogurt (if dairy is tolerated).
Dinner:Grilled turkey with quinoa and steamed green beans.
Foods to Include and Avoid
Foods to Include
Starches and Grains
White rice, plain pasta, and boiled potatoes.
Oatmeal and cream of rice.
Proteins
Skinless poultry, lean fish, and eggs.
Plant-based options like lentils and tofu (if tolerated).
Fruits and Vegetables
Bananas, applesauce, and peeled pears.
Steamed carrots, zucchini, and green beans.
Probiotic-Rich Foods
Yogurt with live cultures (dairy or non-dairy).
Kefir and fermented vegetables.
Foods to Avoid
Dairy Products
Milk, cheese, and cream (if lactose intolerant).
High-Fat Foods
Fried and greasy foods.
Sugary Foods
Sweets, sodas, and desserts.
Caffeinated and Alcoholic Beverages
Coffee, tea, energy drinks, and alcohol.
The Importance of Gradual Reintroduction
As symptoms subside and the infection clears, you can gradually reintroduce more complex and fibrous foods into your diet. Monitor your body’s response and avoid reintroducing too many new foods at once. A slow transition helps prevent irritation of the healing gut.
Tips for Long-Term Gut Health Post-Giardiasis
Continue Probiotic Use
Maintain a diet rich in probiotics to ensure a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support overall health.
Avoid Re-Infection
Practice good hygiene, avoid drinking untreated water, and wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While diet and medications like Nizonide 500mg are effective in treating giardiasis, persistent symptoms may require additional medical attention. Consult your healthcare provider if symptoms worsen or do not improve after completing treatment.
Conclusion
Recovering from giardiasis requires a combination of effective medical treatment, such as Nizonide 500mg, and a supportive diet tailored to your digestive needs. Staying hydrated, eating easily digestible foods, and avoiding triggers are essential steps to recovery. By following these dietary guidelines, you can accelerate healing, restore gut health, and prevent future episodes of giardiasis. Always consult your doctor or a nutritionist for personalized advice based on your specific condition.
What's Your Reaction?
















